Reduce High Frequency Distortion
 KRF filters use a combination of high frequency inductors and capacitors to reduce noise in the critical 150 kHz to 30 MHz frequency range. The inductors act as open circuits and the capacitors act as short circuits at high frequencies while allowing the lower power line frequencies to pass untouched.
KRF filters use a combination of high frequency inductors and capacitors to reduce noise in the critical 150 kHz to 30 MHz frequency range. The inductors act as open circuits and the capacitors act as short circuits at high frequencies while allowing the lower power line frequencies to pass untouched.
KRF filters assist with cost effective compliance to EMC directives, in a compact, efficient, light-weight design. The high common mode and differential mode reduction in the critical 150 kHz to 30 MHz frequency range ensures that potential interference from AC drives is reduced or eliminated.
Non-Linear Loads
Non-linear loads can draw harmonic current from the source, resulting in harmful high frequency noise. There are many pieces of equipment that can generate EMI, variable frequency drives included. In the case of variable frequency drive, the electrical noise produced is primarily contained in the switching edges of the PWM controller. Increases in switching frequencies also increase the effective edge frequencies produces, thereby increasing the amount of electrical noise.
Filter Terminology
EMC Filter
The KRF is an EMC (Electro-Magnetic Compatibility) Filter which allows electrical and electronic equipment to operate without affecting or be affected by other electrical or electronic equipment.
EMI Filter
The KRF is also considered an EMI filter or RFI filter. The terms EMI and RFI are often used interchangeably. EMI (Electro-Magnetic Interference) is actually any frequency of electrical noise, whereas RFI (Radio Frequency Interference) is a specific subset of electrical noise on the EMI spectrum. Conducted EMI is unwanted high frequencies that ride on the AC wave form.
Performance
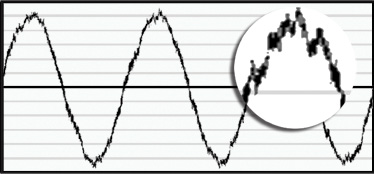
Before KRF
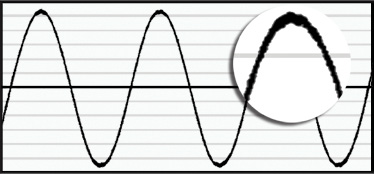
After KRF
Features of the KRF
- Reduces interference
- Protects sensitive equipment
- Eliminates drive cross-talk
- Finger Safe in high voltages
- Advanced 2-stage filtering
- Lightweight and compact
- Available in sizes from 8 – 2,500 Amps
- Available in 480 V, 520 V, 600 V, 690 V, and 760 V
- cULus Listed and ENEC marked
Typical Applications
- Motor Drives
- Elevators
- Commercial Buildings
- Wind Farms
- Photovoltaics
- UPS
- Power Supplies
Recent developments in power conversion devices like AC drives include increases in switching frequencies. The ultra-fast switching devices now used in drives enable greater efficiency, greater motor control and cost effective packaging. As switching frequencies increase, the effective edge frequencies produced and delivered to the line and load also increase. Control of the emission of these frequencies is often a critical factor in a quality drive application. Manufacturers, integrators, sellers or users of drives may be required to comply with electromagnetic immunity standards such as the FCC 15 – Sub-part J, CE (CISPR 11) EMC directive and IEC 801-X. Conducted noise output (db uV).
KRF Series 3 Phase EMC Power Line Filters assist with cost effective compliance to EMC directives, in a compact, efficient and lightweight design. High common mode reduction in the critical 150 kHz to 30 MHz frequency range assures that the potential for interference from AC drives is reduced or eliminated.
Application Notes
EMI filters are current rated devices. Therefore, in order to apply one, you simply need to know the voltage and the full load amps of the drive with which it will be used (See NEC Table 430-150 for HP/Current calculations). No de-rating or re-rating is necessary when applying a KRF Series filter to a voltage that is equal to or less than its rated voltage.
Most electrical noise generated by AC drives is common mode noise. Hence, for peak filter performance, a low impedance, high frequency ground is essential. To obtain this type of grounding, a conductor wire composed of a high quantity of very fine strands must be used. Conductor wires of this nature include battery braid wire, ultra flexible welding cable, or Litz wire. Also, as high frequency electrical noise can radiate, input and output filter leads should be routed separately.
EMI filters are available with convenient termination options. The last 2 letters of the part number determine the termination type. They are: TB=Terminal Block and CB=Copper Bus. See part number table for standard assignments.

